

The baby’s liver makes AFP, and high levels leak into the mother’s blood if anencephaly is present. The AFP test detects higher levels of this protein. One of the tests in the quad marker screen is for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). Your provider takes a sample of your blood and sends it to a lab for testing.
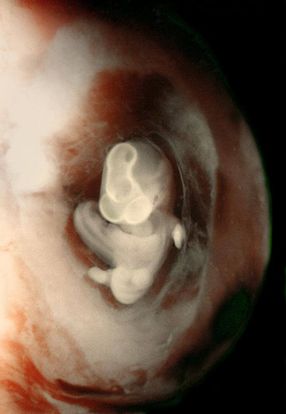
Quad marker screen: This blood test checks for neural tube defects and genetic disorders.Providers can also diagnose anencephaly at birth based on the newborn’s appearance. The rest of the baby’s body continues to form and grow as the pregnancy progresses.ĭuring pregnancy, your healthcare provider may order tests to look for signs that might indicate a neural tube defect. Like all neural tube defects, anencephaly occurs during the third and fourth weeks of pregnancy. Without a closed tube, the brain and skull don’t develop. The neural tube is a flat piece of tissue that grows into a tube and forms the brain and spinal cord. Sometimes called “open skull,” anencephaly happens when the upper part of the neural tube doesn’t close completely during the baby’s development. Opioids include heroin (an illegal drug) and prescription painkillers such as hydrocodone. Opioid use: Taking opioids during the first two months of pregnancy can cause NTDs.Obesity: Women who carry excess weight before pregnancy have a higher chance of having a baby with anencephaly or another NTD.

Some of these drugs also treat migraines and bipolar disorder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
